Content source: China Energy Storage Network PV-Tech

3060
In-depth analysis of household energy storage market demand
Global: Europe’s destocking growth slows down, while emerging markets take over and grow rapidly
From the perspective of the global market, the global household storage market will have 15.6GWh of newly installed capacity in 2022, a year-on-year increase of 136.4%, more than doubling growth, and is expected to maintain a sustained rapid growth trend in the medium term.In terms of installed capacity, Europe, the United States, Japan, and Australia are the world's most important household storage markets, with a total of approximately 60% of newly installed capacity in 2022. In 2022, Europe's newly installed household energy storage capacity will be 5.68GWh, accounting for 36.4% of the global market. In addition, emerging markets such as South Africa and Southeast Asia also have strong demand drivers for household savings. They have shown high growth over the past 23 years, which may provide new growth for the global household savings industry in the future. Next, let’s look at the situation in each major regional market.
Europe: Tight energy supply, high electricity prices + strong policies shape household savings economics
The European energy storage market is mainly driven by the demand for energy self-control and high economics. The European electricity spot market price is determined by energy supply and demand. In 2022, geopolitical conflicts disrupted European natural gas supply and European electricity prices soared. Amid high electricity prices and unstable supply, demand for household savings will surge in Europe in 2022.
In the European energy storage market, Germany and Italy account for nearly 70% of the market. According to SolarEurope, the new installed capacity of household storage in Europe in 2021 is 2.29GWh, +106.8% year-on-year, and the cumulative installed capacity is 5.4GWh. In 2022, the top four newly installed household savings in Europe are Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and Austria. Among them, Germany is still the region with the highest installed household savings in Europe, accounting for 42%. The proportion of newly installed household savings in Italy has increased significantly, compared with 27 %.
Since the beginning of this year, electricity prices in European countries represented by Germany have fallen. The current electricity price has been restored to the 2021 level. The electricity price in Germany, Italy and the UK is around 0.4 euros/kWh, and household storage is still economical. In addition, the energy crisis has increased the determination of European countries to transform their energy sources. It is expected that the demand for new energy construction and energy storage facilities will continue. In order to achieve independent and controllable energy and achieve the long-term goal of carbon neutrality, many European countries have adopted various types of policies to encourage the development of household savings. With strong policy leverage, the economics of household savings in Europe has been further amplified.
The EU launched a "REPowerEU" energy plan in May 2022, which proposed to increase the renewable energy share target to 45% in 2030. In the interim agreement in 2023, the final target was set at 42.5%. Under the general framework decided by the European Union to ensure energy security and promote the development of renewable energy, European countries have actively adopted various types of policies such as government subsidies, tax exemptions, and financing support to promote the installation of new energy equipment. Among them, distributed installed capacity is an important component, bringing additional demand for household energy storage.
As the main country in energy storage construction in Europe, Germany has taken the lead and launched a combined attack to support household savings. Germany’s support for household savings originated earlier, using a combination of financing, taxation, subsidies and other policies.
At present, Germany has two latest main support policies for household storage: First, the "German Renewable Energy Law (EEG 2023)": for household solar energy storage, the remaining grid-connected electricity price has been increased, and the grid-connected subsidy can reach a maximum of 13.4 euros. points/kWh. The installed capacity limit for paying taxes and fees for household energy storage has been increased from 10kW to 30kW. The second is the 2022 Tax Bill: Germany exempts some of the income tax on the feed-in electricity price, exempts the import, purchase, and installation of small rooftop photovoltaic and energy storage systems from the 19% value-added tax, and simplifies the value-added tax exemption process. The two policies have reduced the payback cycle of household optical storage equipment by increasing electricity sales revenue and reducing system costs, thus improving the economics of household storage in Germany.
In 2023, with the decline in natural gas prices and the decline in residential electricity prices, coupled with the continued destocking of European dealers, performance will be dragged down, and the market will be worried about the actual demand in Europe. However, the actual installation rhythm of the European market in 2023 still shows a strong trend. According to statistics from ISEA&RWTH Aachen University, Germany's household storage installed capacity from January to August 2023 was 3.04GWh, +158.0% year-on-year. According to ANIE statistics, in the first quarter of 2023, Italy’s energy storage installed capacity was 1.09GWh, +296.0% year-on-year. We believe that the slowdown in shipments in 2023 is mainly due to the temporary impact of destocking.
In 2023, as natural gas prices fall, residential electricity prices fall, and European dealers continue to destock, dragging down performance, and the market becomes worried about the actual demand in Europe. However, the actual installation rhythm of the European market in 2023 still shows a strong trend. According to statistics from ISEA&RWTH Aachen University, Germany's household storage installed capacity from January to August 2023 was 3.04GWh, +158.0% year-on-year. According to ANIE statistics, in the first quarter of 2023, Italy’s energy storage installed capacity was 1.09GWh, +296.0% year-on-year. We believe that the slowdown in shipments in 2023 is mainly due to the temporary impact of destocking.
The current rate of return on energy storage is still relatively high. Considering that compared with 2021, the current product preparations are more diversified, the cost of raw materials such as batteries has begun to decline, and user education is more sufficient, European household storage still has high growth momentum. The European energy storage market is mainly driven by the demand for energy self-control and high economics. It is expected that shipments will return to rapid growth in 2024, and there is still a lot of room for improvement in the penetration rate of household storage in Europe.
The aging of the U.S. power grid in recent years has brought about demand for distribution and storage, and household photovoltaic storage has become the second source of electricity for households. The underlying driving factor for the demand for household savings in the United States is that the US power grid is aging and power outages are prone to occur during severe weather. At the same time, the latest ITC and NEM3.0 policies in the United States are increasing the economics of household savings. In addition, the structure of houses in the United States is mainly single-family, with ample roof area, giving sufficient space to release the demand for household savings, and the growth of household savings can be expected in the future.
According to reports from CNBC and the Energy Bureau, most of the power grid in the United States was built in the 1960s and 1970s, and more than 70% of the transmission system is more than 25 years old. When operating at high load or when the external environment is under pressure, the power grid is prone to short circuits and other conditions. , causing a power outage.
According to EIA statistics, each user in the United States will experience power outages for more than 7 hours in 2021, of which power outages due to weather conditions last for more than 5 hours. According to DOE statistics, there will be 390 power outages in the United States in 2022 and 167 power outages in the first half of 2023. According to NOAA, as of the end of August 2023, 23 severe meteorological disasters with a single impact of more than US$1 billion have occurred in the United States this year, exceeding the record set in the entire year of 2020 (22). Frequent power outages due to aging power grids and weather conditions have led American home users to seek the protection of photovoltaic and energy storage facilities.
On August 16, 2022, Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) worth a total of US$750 billion, which will be officially implemented in 2023. The IRA extends the ITC time limit to 2035. For the first time, independent energy storage is included in the scope of tax deductions in IRA, clarifying that independent energy storage greater than 3kWh can also apply for ITC deductions. The IRA subsidy time and scope for ITC have been relaxed, which has reduced early concerns about subsidy fading. The initial construction cost of U.S. energy storage has dropped significantly, supporting demand.
According to Wood Mackenzie, the newly installed capacity of energy storage in the United States in 2022 will be 4.80GW/12.18GWh, +34.2%/11.8% year-on-year. Among them, the newly installed capacity of grid-level/household/industrial and commercial energy storage accounts for 86%/11%/3% respectively in terms of energy capacity. The projects are mainly large-scale storage in front of the meter, and household storage maintains steady growth. In 2022, the United States added 631MW/1537MWh of household storage capacity, +45%/36% year-on-year; in 23Q1 it was 155.4MW/388.2MWh, +7%/+36% year-on-year. With the demand for backup power and increasing policies, we are optimistic that the household storage market in the United States will continue to grow rapidly.
Australia: The ratio of storage/solar assembly has increased sharply, and household storage has become economical
Driven by high electricity prices and incentive policies, Australian household savings have become economically viable. Australia has a high cumulative installed capacity of distributed photovoltaics. On this basis, the ratio of energy storage to photovoltaic installations will grow rapidly in 2022, mainly due to the significant improvement in the economics of household storage due to rising energy prices and federal solar and energy storage incentives. Australia's household savings market will develop rapidly in 2022. According to SunWiz statistics, the Australian household storage market will achieve 47,100 new installed units in 2022, with an installed capacity of 589MVh, a year-on-year increase of 55.72%/76.88% respectively.
Sufficient lighting conditions and favorable policy environment have supported the rapid growth of distributed photovoltaics in Australia. It is reported that Australia's lighting resources rank first in the world. At the same time, Australian photovoltaic equipment can produce more electricity and the cost of photovoltaic power generation per unit is lower. At the same time, the government provides FIT subsidies for household photovoltaics. Under the dual favorable conditions of light factors and policy factors, the cumulative installed capacity of household photovoltaics in Australia is high.
The high growth in household photovoltaic installed capacity provides the foundation for household storage installations. At the same time, the record high proportion of photovoltaic assembly is the main source of growth in household storage installations. According to Sunwiz statistics, a total of 47,100 small energy storage units were installed in 2022, and the converted number of new energy storage units/photovoltaic units in that year was about 15.0%, +7.0pct year-on-year. According to Australia Energy Council statistics, there were 21,700 small photovoltaic equipment equipped with storage in 2022, accounting for approximately 46.0% of the total installed energy storage capacity. That is, the proportion of original photovoltaic equipment allocated and stored was approximately 54.0%, accounting for approximately half of each.
According to statistics from the Australian Energy Regulator (NER), the spot price of electricity in mainland Australia reached a peak in the second quarter of 2022, mainly due to the sharp rise in energy prices due to geopolitical conflicts and the continuous shutdown of coal power plants on Australia's east coast due to La Niña-driven rainfall. Affected by other incidents, coal and natural gas supplies are in short supply. Due to rising wholesale prices caused by inflation, geopolitical conflicts and aging power plants, electricity prices may remain on an upward trajectory in the second half of the year. According to AER, starting from July 1, 2023, electricity prices are expected to increase by 20% to 25% year-on-year. The main impact will be on household users and small traders, which may directly stimulate the demand for household energy storage installations.
Many states in Australia provide subsidies for household storage systems to reduce installation costs. Most of the policies used by Australian states include directly providing purchase rebates or providing zero-interest loans to homeowners to purchase energy storage equipment. With the support of subsidy projects, it is more feasible and economical for households to install household storage systems, and the number of household storage installations has increased rapidly in the past few years.
South Africa: The power supply has seriously deteriorated, and electricity needs self-distribution and storage.
The electricity shortage has had a serious impact on residents' lives, and South African households have chosen to proactively distribute and store electricity to ensure electricity consumption. Unlike Europe and the United States, the development of household savings in South Africa mainly comes from the spontaneity of households and is less affected by policy drivers. South Africa's traditional power supply is a seller's market under a high degree of monopoly. It is affected by multiple adverse factors and the power shortage problem is difficult to solve in the short term.
According to Eskom's annual report, South Africa will have more than 200 power outage days in 2022, with power outages lasting up to 1,900 hours. The situation has further deteriorated so far in 2023, and South Africa's power crisis has entered a "disaster state". Distribution and storage are an important and effective way to ensure power consumption. In the face of frequent power outages, South African households proactively use photovoltaic and storage equipment to seek power security.
The government's renewable energy incentive policies have achieved significant results, and domestic inverter exports have jumped significantly. The energy crisis has been superimposed and under pressure from developed countries, the government has actively promoted low-carbon transformation and renewable energy investment.
In July 2022, the South African government announced that it would exempt all embedded power generation (distributed self-generation) licenses and introduce a feed-in tariff (FiT) mechanism for rooftop solar to incentivize solar module owners to sell excess power to the grid.
In February 2023, the government announced a photovoltaic tax subsidy of up to 4 billion rand (approximately US$210 million). Household users who install rooftop photovoltaics can apply for a 25% tax rebate on the purchase cost of solar panels. The two policies have played a significant stimulating role. When the corresponding policies were introduced, China's exports of South African inverters saw two significant jumps.
Policy stimulus coupled with the power crisis, the growth of South Africa's household storage market is expected to be sustainable. In order to alleviate the power crisis, the South African government announced that national electricity prices will increase by 18.56% and 12.74% respectively in 2023 and 2024, in order to curb residential electricity demand.
Judging from the latest data in 2023, China's exports of inverters to South Africa from January to July 2023 totaled 3.108 billion yuan, +487.7% year-on-year; the average price was 2,152.0 yuan/unit, +105.6% year-on-year from January to July 2022. China The price and volume of inverters exported to South Africa increased. Considering that South Africa is also following the global pace and gradually getting rid of its dependence on coal power generation, the large-scale construction of coal-fired power stations is blocked, and the power problem cannot be solved in the short term, it is expected that the high growth rate of the South African energy storage market will be relatively sustainable.
Southeast Asia: Fragile power grid + extreme weather trigger power consumption contradictions
With a fragile power grid, extreme weather intensifies power consumption conflicts, and the energy storage market is growing rapidly. The overall power facilities in Southeast Asia are fragile, and the power grids in some archipelago countries are mainly off-grid. In addition, island residents are scattered and overhead lines are poorly regulated. The overall power grid situation is more suitable for the development of distributed rooftop photovoltaic energy storage.
According to the established policies of the ten countries in the ASEAN region, three-quarters of the growth demand will be met by fossil fuels, resulting in a 35% increase in carbon dioxide emissions. At present, Southeast Asia is still dominated by coal-fired power supply, and the energy storage market in Southeast Asia is still in its early stages of development. According to incomplete statistics, among the new new energy storage projects put into operation in the world in 2022, the Southeast Asian market will account for 2% of the global market, which is a small proportion, but demand will grow rapidly in 2023. The main energy storage markets in Southeast Asia include Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, etc.
In 2023, the amount of China's inverter exports to Southeast Asia increased significantly. Market demand has increased significantly in 2023. From the perspective of inverter export volume, from January to July 2023, China exported a total of 1.680 billion yuan of inverters to Southeast Asia, +86.7% year-on-year. In terms of countries, China's main inverter exporting countries in Southeast Asia are Thailand, Malaysia, and the Philippines. The export value from January to July accounted for 33.7%/17.6%/14.4% of the total Southeast Asia export value respectively.
Under the influence of El Niño climate, Southeast Asia is in a deep power shortage crisis. Countries such as Thailand and the Philippines, which mainly rely on diesel, natural gas, coal and other fuels for power generation, have also experienced large-scale power cuts and blackouts due to insufficient supply of power generation fuels, which have seriously affected residents' lives and production activities. Southeast Asia's power grid is regionally mismatched, incompletely developed, and its population is dispersed, which is not conducive to centralized power supply. Distributed household optical storage is more suitable for local needs in Southeast Asia.
European household savings: Growth slows down, Germany leads the way
In recent years, the European market has been affected by rising energy prices. Residential electricity prices have soared, and the economics of energy storage have been reflected. Driven by the anxiety of the energy crisis, various regions in Europe have introduced policies to develop clean energy and accelerate the pace of energy transformation to ensure energy supply. The demand for household energy storage continues to grow.Nowadays, with the impact of falling electricity prices, rising interest rates, policy changes and other factors, the golden age of household savings seems to have shrunk. On the one hand, new and old domestic players are frantically "expanding production capacity", and on the other hand, overseas dealers are "destocking". Although household savings still have certain opportunities to increase penetration, its growth rate has quietly slowed down.
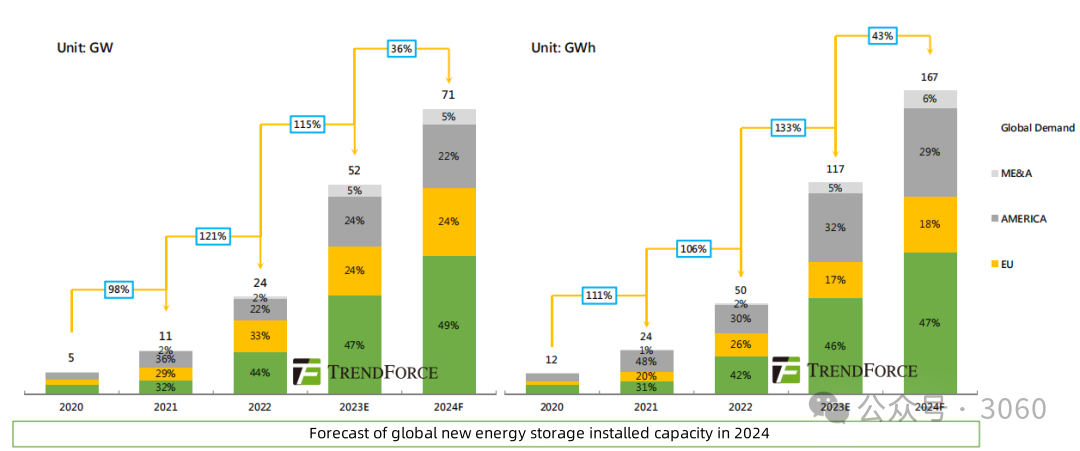
01. Global household savings development expectations in 2024
Looking forward to 2024, judging from the growth rate of global household storage, the Energy Storage Research Center of TrendForce predicts that the subcategories of new global energy storage installations in 2024 will appear - industrial and commercial storage (93%/112%) > Large savings (39%/43%) > Household savings (4%/11%) trend. Among them, household storage, in the context of both the decline in electricity prices and natural gas prices, residents' urgency for installing power has weakened, and its growth rate has slowed down significantly compared with 2023, with a year-on-year growth of only 11%.
From an incremental point of view, the global new energy storage installed capacity in 2024 will show a trend of large storage (53GW/130GWh) > household storage (10GW/20GWh) > industrial and commercial storage (7GW/18GWh). Since household savings started earlier and the profit model is relatively mature, there is still room for growth. Therefore, the increase in household savings in 24 years will still be slightly higher than that of industrial and commercial savings.
02. European household savings: growth slows down, Germany leads the way
Due to the high degree of power grid connectivity in Europe, the demand for large storage is not as strong as in other regions. Therefore, unlike other markets where large storage has an absolute advantage, the European market presents a unique situation where the ratio of pre- and post-meter energy storage is close to 1:1. , becoming the world’s first household storage market. As Europe actively promotes energy transformation, the scale of European household storage installed capacity has increased rapidly. According to IHS Markit data, the growth rate of household storage installed capacity in Germany and Italy is higher than the European average, and their shares rank first and second respectively; Germany accounts for more than 70%, making it the country with the largest household storage market in the world.
The European household savings market is currently highly concentrated, with the top five countries accounting for about 90%. However, as household savings gradually become more popular in other European countries, the growth pace of leading countries has diverged. France and Spain have surpassed Austria and Tuscany to join Europe. The top five in household savings share.
Europe mainly relies on external supply of energy, and residents’ electricity prices are much higher than the global average and higher than developed countries in other regions. For example, Italy has one of the highest electricity prices in the world. The spot price of electricity in Europe is closely related to natural gas. Driven by the energy crisis, electricity prices will rise to an all-time high in 2022, with the highest residential electricity price exceeding 0.7 euros/kWh, which is approximately 10 times the domestic electricity price in China. Although natural gas prices will obviously fall in 2023, electricity demand will return to pre-epidemic levels, and residential electricity prices in major European countries are still much higher than in 2020.
In addition, various taxes, surcharges and other components in Europe also lead to high costs, such as grid transmission and distribution costs, renewable energy surcharges, value-added tax, electricity tax, etc. Taxes and fees in countries such as Britain, Germany, and Italy account for 30% of the electricity price~ 60%%. Affected by the price of natural gas and the certain rigidity of power grids and taxes, European household electricity prices are higher than the cost of household solar energy storage.
In terms of policies, since European countries are at different stages of optical storage development, their policy priorities are also different. Take Germany as an example. As the main country in energy storage construction in Europe, Germany has preemptively launched a combined attack to support household storage. Germany’s support for household savings originated earlier, using a combination of financing, taxation, subsidies and other policies. The following are some recent relevant policy developments in Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom.
Annual Tax Bill of the German Bundestag
▲ Time: Effective in 2023;
Contents:
① Household photovoltaic systems less than 30kW are exempt from income tax (14-45%);
② Photovoltaic systems of multi-family conjoined mixed-use properties less than 15kW are exempt from income tax;
③The purchase of photovoltaic systems & energy storage systems is exempt from value-added tax (VAT, 19%), which actually simplifies the VAT exemption process;
Comments: Income tax exemption stimulates the household market.
German KFW Bank Solar Power for Electric Cars integrated light storage and charging subsidy
▲Time: Released in September 2023;
Content: Provide financial subsidies for household light storage and charging integrated systems, with a total amount of 500 million pounds;
Comment: The subsidy can account for 25% of the total cost; the maximum subsidy for a single household is 10,200 pounds, and a minimum of 50,000 systems can be subsidized. The number of household storage systems installed in Germany in 2023 is about 400,000-500,000, and the subsidy is limited.
Italian Government Ecobonus Subsidy
▲ Time: Released in 2020, retired in 2023
▲Content: The tax exemption for household energy storage equipment was increased from the original 50-65% to 110% (extended to 2024), and is paid in 5 installments over a 5-year period; it was later changed to gradually decrease to 90% in 2023, 2024, and 2025. %, 70%, 65%.
Comments: Subsidies are weakening and the margin is downward.
New tax exemption policy for energy storage batteries in the UK
Time: Launched in December 2023, implemented on February 1, 2024;
Content: The 20% value-added tax on the installation of battery energy storage systems (BESS) will be canceled from February 1, 2024, which was previously limited to batteries installed at the same time as solar panels;
Comments: Energy storage systems have begun to be exempted from tax separately, which is beneficial to household use of light and storage.
Global Household Energy Storage Market White Paper: Market Analysis of Germany, Italy, the United States, Japan, Australia and China

Figure 1: BNEF Cumulative Residential Energy Storage Expectations Figure 2: 2023 Solar Cell Installation Rates, Selected Markets
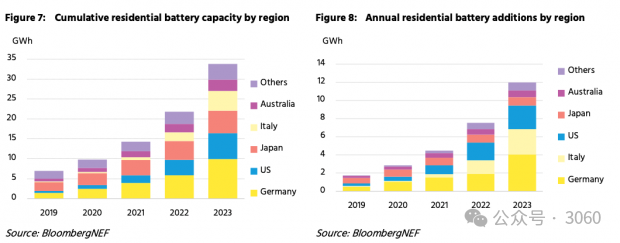
Figure 7: Cumulative household battery capacity (by region) Figure 8: Annual new household batteries (by region)
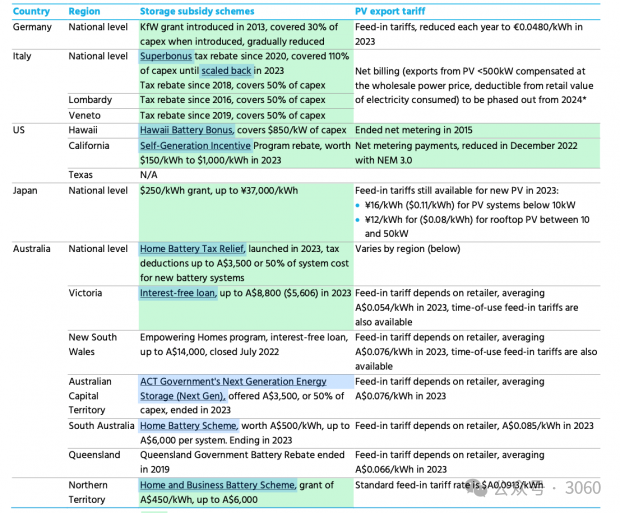
Table 1: Comparison of residential battery storage drivers across key regions. Source: Bloomberg NEF.
Note: Green = the main driving factor supporting the popularization of household energy storage.
*= Italy’s net billing policy for new PV systems will end on January 1, 2024, while existing systems will need to be gradually converted to a lower compensation plan by the end of 2024, with a compensation amount of approximately €100/MWh, Depends on production time and region. Japan’s photovoltaic output electricity price applies to photovoltaic systems of 10-50kW.
Currently, the adoption of residential battery storage in other markets is limited by economic feasibility. Growth over the next five years will be driven by both economics and policy, with battery costs falling and countries supporting the use of batteries to manage the growth of rooftop solar and electric vehicles.
The white paper points out that supporting policies such as subsidies and authorizations have promoted the popularity of household battery energy storage in major markets. Rising consumer interest in increasing solar self-consumption and backup power also plays a role. However, batteries are still too expensive for most consumers to purchase without some form of support. Therefore, due to the relative lack of supporting frameworks, cumulative residential battery capacity in all other markets combined will be less than 1.2GW/2GWh by the end of 2023.
Over time, demand will grow in other markets. Battery costs will fall, and governments will phase out policy mechanisms such as feed-in tariffs and net metering. When these policies are phased out, consumers will be more inclined to install batteries to ensure maximum utilization of solar power.
In major markets, household battery adoption primarily begins with battery storage subsidies. Other key factors driving battery demand growth in some markets include the phasing out of photovoltaic output tariff frameworks, which reduces incentives to export excess solar power and customer interest in backup power. Table 1 lists the key policy decisions supporting household battery demand in the largest markets.
Let’s take a closer look at the situation in several leading countries where the household battery energy storage market is developing rapidly.
Germany
Germany is the earliest large-scale household battery market. In May 2013, the German government launched a subsidy program administered by KfW that provides subsidies for energy storage systems installed alongside new or existing solar systems under 30kW. This has propelled Germany into the world's largest market for residential solar and batteries, with installation rates remaining stable even as subsidies have been reduced year by year.
In 2022, the installation rate of rooftop solar cells will exceed 75%, one of the highest installation rates in the world.
Subsidies have supported the market's growth for more than a decade, but they have slowly shrunk and are no longer the main driver. Instead, the market is now driven by customers committed to increasing their own on-site solar consumption, as they can save more than €0.30 per kilowatt-hour by purchasing electricity from the grid, while exporting solar power for less than 0.30 euros per kilowatt-hour. 0.05 euros.
Italy
In 2022, Italy will become the second largest market, accounting for more than 20% of the global new market in 2021 and 2022. In 2022, the adoption rate of rooftop solar cells is 77%, up from 11% in 2018. This follows the launch of Italy's extremely generous "Super Bonus" subsidy program in 2020, which covers 110% of all home energy improvement-related costs.
After the program launched in 2020, adoption rates increased dramatically. But after the "super bonus" program was scaled back in early 2023, adoption rates suddenly dropped. Unlike Germany, the Italian government quickly withdrew this support program, and the market was unable to sustain growth without the program.
BNEF expects adoption rates to remain moderate. The 50% state tax rebate scheme remains in place, which had already given a boost to a number of projects across Italy before the "super bonus" scheme was introduced. Consumers also receive regional subsidies. For example, in Lombardy, solar-battery products enjoy a 50% tax rebate starting from 2016.
USA
The U.S. residential battery market is very fragmented, as state-level policies are the largest determinant of battery adoption and can vary widely.
California, Florida and Texas are the markets with the largest number of system installations, with installation rates of 9%-12% in 2022 and expected to rise significantly in 2023. Installation rates in these markets are primarily driven by demand for backup power, and grid disruptions due to extreme weather events are becoming a huge concern for customers.
California, in particular, has emerged as an attractive market over the past year due to changes in solar net metering policies that encourage consumers to pair batteries with existing PV systems. Demand in California is also supported by the California Self-Generation Incentive Program, which provides subsidies of $150-$1,000/kWh for residential batteries.
Although Hawaii is a smaller market in terms of the number of systems installed, its installation rate is among the highest in the country. Since power companies only allow utility systems to transmit power to the grid, about 96% of residential PV installations will be equipped with batteries in 2022. Consumers are even more motivated to install batteries through targeted subsidies provided by the Hawaii Battery Bonus Program.
BNEF expects adoption to increase in the United States over the next five years due to more frequent outages, lower prices for rooftop solar output, the introduction of time-based evening peak retail electricity prices, higher peak demand charges and demand response compensation.
Japan
Driven by subsidy programs, the household battery market has become Japan's largest energy storage market, with newly installed batteries receiving subsidies of up to 37,000 yen ($250)/kWh.
Many Japanese households with solar modules installed will end their initial 10-year feed-in-tariff contracts in 2023-2030, so the remuneration (if any) they receive for exporting solar power will be significantly less, meaning people have to add existing self-consumption PV systems. motivation.
Australia
Australia's growing household battery market has been spurred by soaring electricity prices in many states, subsidies and resilience issues. Nationwide, cell adoption in new photovoltaic installations will jump to nearly 15% in 2022 from about 8% in 2021. Installation rates remain relatively low compared to European markets as the continued use of feed-in tariffs (transmission payments provided by retailers) limits solar adoption.
While most Australian solar owners receive flat transmission payments, starting in Victoria, electricity retailers are introducing time-varying rates, which is promising for batteries.
Under this scheme, these owners could be paid higher or lower depending on the time of day they export solar power to the grid, which would encourage them to install batteries to store excess solar power during the day and export it at night when prices are typically higher. . Other Australian states are likely to follow suit, starting with South Australia. The state has been exploring rates for different time periods since 2020.
China
China's household battery market has struggled to take off due to China's relatively low electricity rates and limited concerns about energy supply resilience (low blackout rates).
In the first half of 2023, the average electricity price for Chinese households was less than 0.530 yuan ($0.076)/kWh, which is approximately equivalent to 50% of the average U.S. household electricity price and 15% of the German household electricity price. Due to cross-subsidies from industrial and commercial end-users, household electricity prices in China are artificially low. Low electricity prices make consumer energy storage projects economically unattractive.
For China's electricity users, the losses caused by grid outages are also less worrying, which also reduces the emphasis on energy storage. Without further incentives, China's household energy storage market is expected to remain small by 2030.